|
|

2004 fourth warmest year
in over a century
NASA Release February 8 2005
Last year was the fourth warmest year on average for our planet since the late 1800s,
according to NASA scientists.
The 2004 average temperature at Earth's surface around the world was 0.48 degrees Celsius
or 0.86 Fahrenheit above the average temperature from 1951 to 1980.
Globally, 1998 has proven to be the warmest year on record, with 2002 and 2003 coming
in second and third respectively. There has been a strong warming trend over the
past 30 years, that has been shown to be due primarily to increasing greenhouse gases. |
| |
 |
Some of the changes in climate are due to short-term factors like large volcanic eruptions
that launched tiny particles of sulfuric acid into the upper atmosphere (stratosphere) in
1963, 1982, and 1991. These natural events can change climate for periods ranging from months
to a few years. |
| |
|
Scientists use temperatures taken on land and on surfaces of the oceans. Weather
stations provide land measurements, and satellites provide sea surface measurements.
Other natural events, like El Ninos, when warm water spreads over much of the tropical
Pacific Ocean, also have large short-term influences on climate. The high global
temperature in 1998 was associated with one of the strongest El Ninos of recent
centuries, and a weak El Nino contributed to the unusually high 2002-2003 temperatures.
Even though big climate events like El Nino affect global temperatures, the increasing
role of human-made pollutants plays a big part.
Earth's surface now absorbs more of the Sun's energy than gets reflected back to space.
That extra energy, together with the weak El Nino, is expected to make 2005 warmer than the years
of 2003 and 2004 and perhaps even warmer than 1998, which was far hotter than any year in the
preceding century.
Another interesting note is that global warming is now large enough that it is beginning
to affect seasons, and make them warmer than before on a more consistent basis.
Compared to the average temperatures from the 1951 to 1980 period, the largest unusually
warm areas over all of 2004 were in Alaska, near the Caspian Sea, and over the Antarctic
Peninsula.
|
 |
|
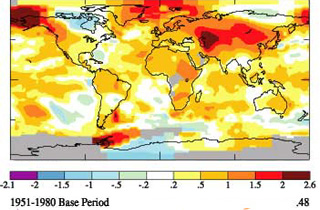
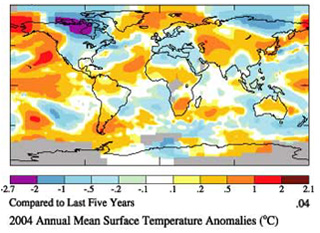
Temperature Comparisons
Top Map: The years of 1951 to 1980 are used as a "baseline" or average for surface
temperatures of Earth's land and ocean surfaces. The top map is color coded to show
the differences from the 2004 temperatures to that period. Yellow to red colorations
indicate areas warmer than the 1951-1980 timeframe.
Lower Map above: 1999-2003 temperatures were matched against the
global 2004 temperatures, and the result is that the yellow and red areas were warmer in 2004,
while the white and blue areas were cooler. Images NASA |
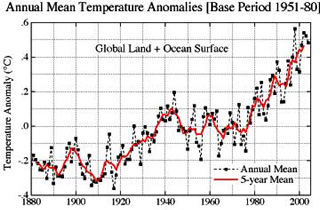
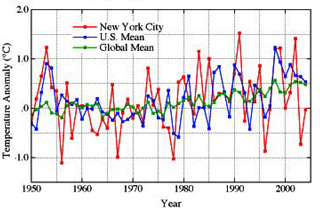
The Warming Trend of Global Surface Temperatures
(Shown above)
Trends of annual surface temperature relative to the 1951-1980 mean: the global mean is shown above
top, and the global-plus-local means immediately above. The upper panel shows that globally
the warmest temperature occurred in 1998 (highest black dot on the top right), while the second and
third warmest years were 2002 and 2003, respectively. As the figure shows, there has been
a strong warming trend over the past 30 years, a trend shown to be due primarily to increasing
greenhouse gases.
Images NASA |
 |
|














 3 degrees: Chief scientist warns bigger rise in world's temperature will put 400 million
at risk
3 degrees: Chief scientist warns bigger rise in world's temperature will put 400 million
at risk




